INTRODUCING
SonoWand Invite™ - Intraoperative 3D Imaging System
SonoWand Invite™ is a single-rack, digitally integrated 3D ultrasound intraoperative imaging system for neurosurgical navigation. The system may also be implemented as a conventional MRI- or CT-based neuronavigation system or as a stand-alone 2D ultrasound scanner.
SonoWand Invite enables you to plan your surgical procedure using standard imported DICOM MRI or CT preoperative images, acquire a 3D ultrasound data set and compare the two modalities prior to opening the dura mater.
During the operation, SonoWand Invite may be implemented to rapidly reconstruct high-quality 3D ultrasound patient image volumes, strengthening your trust and confidence.
SonoWand Invite features an intuitive user-interface displayed on its large touch-screen monitor, maximizing its ease-of-use. This 3D display is a user-friendly tool for improved guidance during both tumor resection and other cerebro-vascular procedures.
The compact design of the system allows for easy storage and transport between operating theaters. Furthermore, it requires no additional investment in costly, specialized surgical tools or shielding in the OR.
From a cost/benefit perspective, the initial cost of SonoWand Invite is not only a fraction of alternative iMRI or CT solution, it saves considerable time spent updating the surgical map.
Navigating with SonoWand Invite™
The SonoWand Invite™ has been designed to perform highly precise neuronavigation regardless of brain shift and anatomical manipulation during surgery. The system allows the surgeon to identify and distinguish lesions from normal brain tissue and surrounding landmarks in a real time, 3 dimensional view.
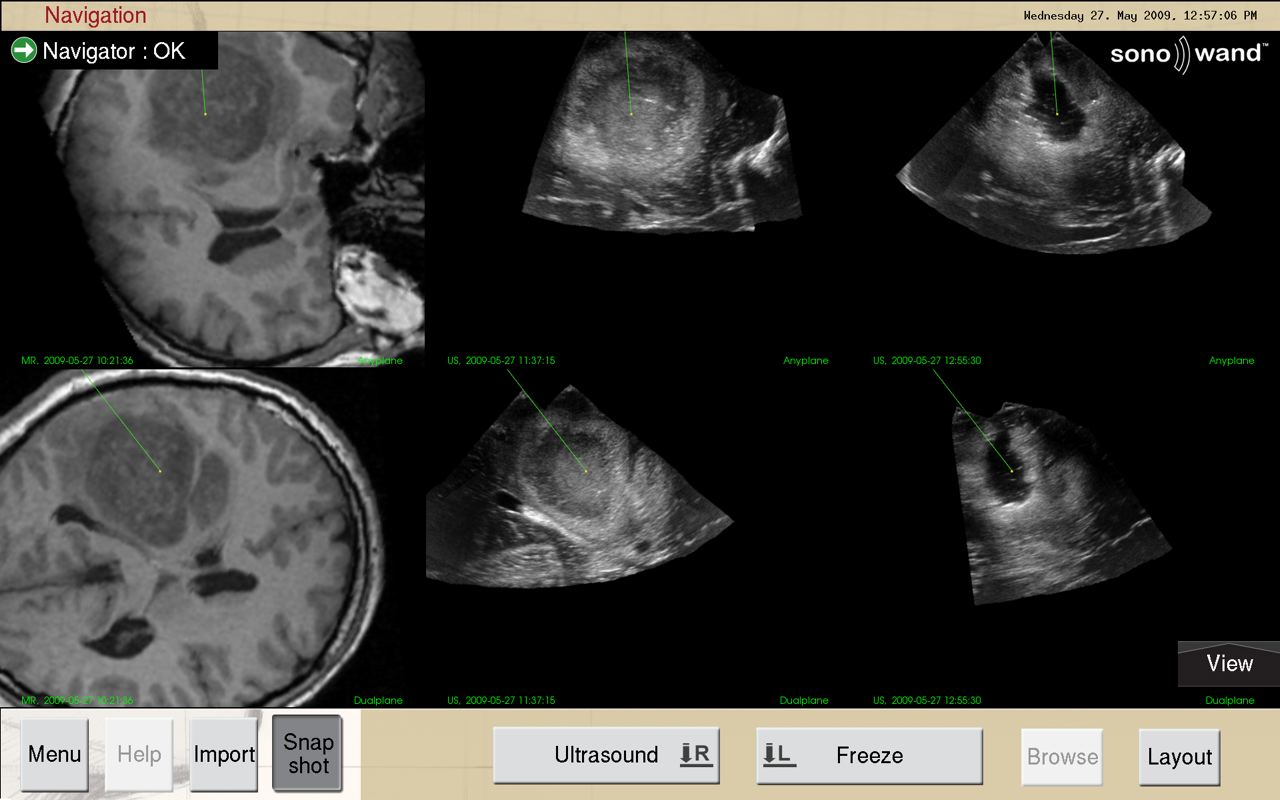
Screenshot taken during surgery (glioma) at the Tartu University Hospital.
The probe range of the SonoWand Invite™ facilitates intraoperative scanning and navigation deep in the parenchyma, superficially in the parenchyma, in the posteria fossa and in the medulla.
Ultrasound angio scans (Power Doppler) in the three dimensions enables detection and localization of vital blood vessels in the navigation scene. This is particularly valuable in minimal invasive surgery and interventional procedures since the risk of bleeding complications presumably can be reduced.

